During the course of Taipei's rapid urban development, natural green spaces have been gradually supplanted by impervious asphalt and concrete surfaces, leading to the loss of natural water retention and infiltration functions. Coupled with the intensifying impacts of climate change, the threat of intense, short-duration rainfall has been exacerbated. To move towards a sustainable Taipei and create a sponge city, the Public Works Department initiated the Sponge City Policy in 2015. This policy outlines Taipei's future vision through "resilient water adaptation," "sustainable water utilization," and "a water-friendly environment." It sets six key objectives: "enhancing urban water circulation," "increasing flood absorption capacity," "diversifying water usage," "ensuring stable water supply and efficient use," "promoting ecological diversity in aquatic habitats," and "enriching water recreation opportunities."
Taipei has a high level of urbanization (photo)
To clarify specific goals, the Public Works Department presented the Public Works Construction Vision Plan in 2018, aiming to build a resilient city through public-private partnerships. The long-term goal is to achieve an average urban rainfall protection standard of 88.8mm/h, which serves as the benchmark for the city's Rainfall Absorption Capacity Enhancement Plan.
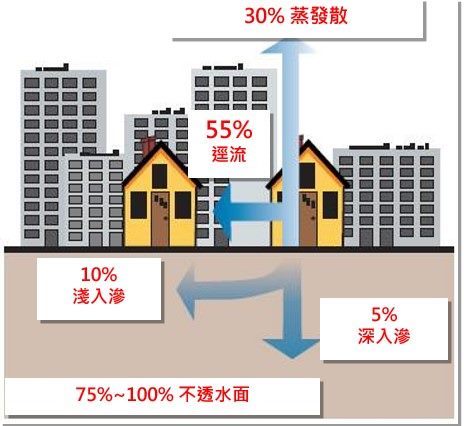
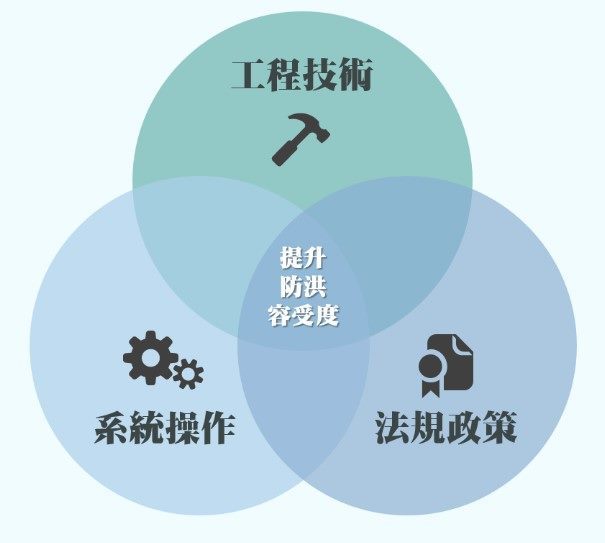
With Taipei's urban areas nearing full development, the existing drainage and flood control infrastructure, while continuously expanded and improved, still faces major challenges. The impacts of climate change have intensified both the volume of floodwater and the extent of water accumulation. Given the limitations in significantly expanding existing facilities, the city must adopt a comprehensive strategy that integrates engineering, system operations, and regulatory measures. This multi-pronged approach aims to enhance Taipei’s flood resilience and achieve the goal of increasing the city’s rainfall absorption capacity, ensuring greater protection against extreme weather events.
Methods and approach for enhancing rainfall absorption capacity (photo)
(I) Develop SOPs and Strategies for Enhancing Rainfall Absorption Capacity
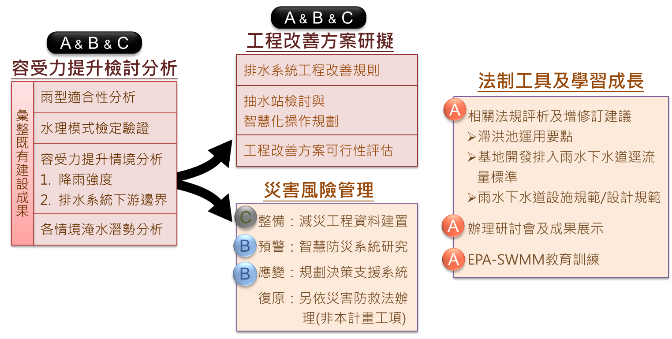
To achieve the set goals, the project is divided into three tender projects: A, B, and C. These cover 78 catchment areas across the 12 administrative districts of Taipei City. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) will be established to define the principles and processes required for the drainage system review. Suitable hydraulic models will be selected for validation, and the cost and economic benefits of proposed solutions will be evaluated. This will provide a clear framework for planning drainage system improvements and developing strategies to enhance the city’s rainfall absorption capacity.
(II) Continuous Advancement of Infrastructure Projects (Example: Wenshan's Five Major Flood Control Projects)
1. For densely populated residential and commercial areas, localized drainage enhancements will be implemented. This includes regular maintenance such as sediment and debris removal from drainage systems and adjustments to improve flow capacity by adding secondary drainage lines and revising drainage zones.
2. Suitable locations within catchment areas will be identified for the installation of aboveground and underground detention basins. These facilities will reduce peak runoff through infiltration and storage methods.
3. Existing pump stations will be replaced with higher-capacity units during their end-of-life upgrades to enhance the city’s flood management capabilities.

(III) Leveraging Big Data to Optimize Flood Control and Drainage Operations
1. Automated Pump Station Operations:
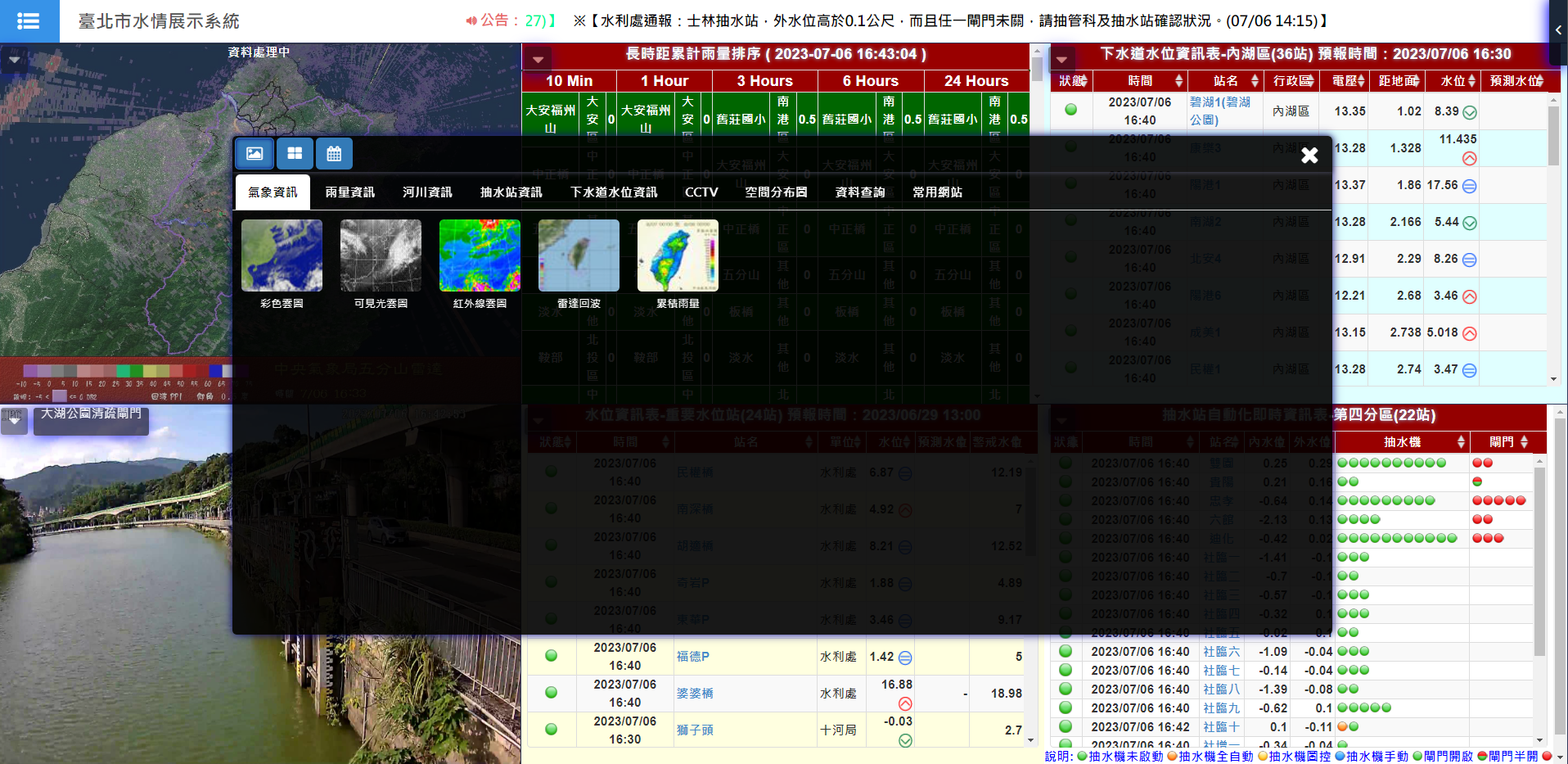
The city has installed 35 rainfall monitoring stations and 152 stormwater drainage water level monitoring stations across the urban area. All water-related data is integrated into the Taipei City Typhoon Preparation Center's water information monitoring system. This real-time data, including rainfall, stormwater, and river levels, is provided to pump station operators or automated control systems, enabling early activation of pump stations during storms to improve drainage efficiency.

2. Hydraulic Information Integration and Open Data:
As the need for disaster prevention information grows, the city continuously integrates meteorological, rainfall, stormwater, pump station, river level, and video monitoring data into a holistic integrated system. The interface and components are constantly adjusted to ensure quick and accurate information access, reducing the risk to citizens' lives and property.
Residents can also use the Taipei City Disaster Prevention app or subscribe to the "TaipeiHEO" LINE official account to receive real-time water information and flood warnings.
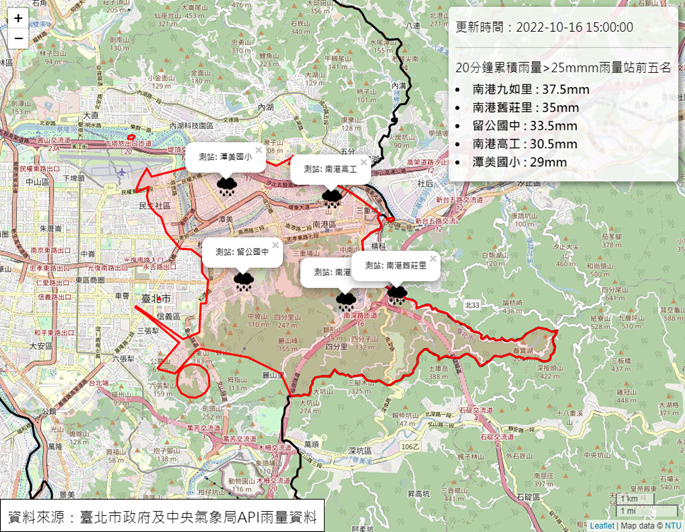
3. Establishing an Urban Flooding Early Warning Mechanism:
With the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme rainfall events, relying solely on real-time observations has proven insufficient. The city is developing an urban flooding early warning system to guide flood control operations and disaster response, providing timely alerts and reducing the impact on citizens.
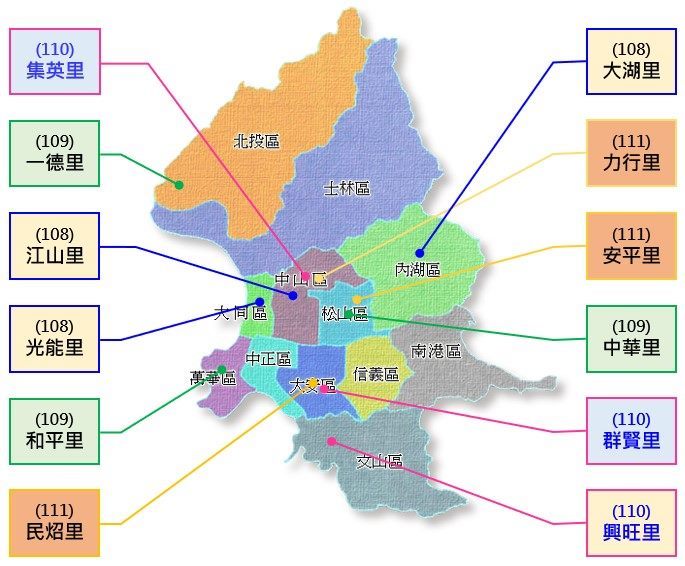
(IV) Promoting Public Participation in Autonomous Disaster Prevention
Before government disaster relief resources can be deployed, it is crucial for communities to be capable of self-reliance and mutual aid and to establish effective flood response mechanisms. Through the "Taipei City Community Resilience to Flood Disasters Program," the city promotes disaster preparedness through various activities, workshops, and expert lectures. These initiatives aim to systematically educate community members on self-resilient disaster prevention, enhancing their capacity to respond effectively to flood-related emergencies. By fostering community cooperation and mutual assistance, the goal is to minimize disaster-related losses.
(V) Public-Private Collaboration to Implement Runoff Mitigation Facilities
To enhance water retention capabilities in urban development areas, Taipei City has introduced the "Taipei City Water Retention Guidelines for Public Facility Land Development" and the "Taipei City Stormwater Drainage Runoff Volume Control Standards for Development Projects." These regulations require both public and private developers to manage and mitigate the increased surface runoff caused by their projects. By leveraging the combined efforts of public and private sectors, the city aims to gradually improve its rainfall absorption capacity, following the principle that small efforts can collectively lead to significant impact.


![Taiwan.gov.tw [ open a new window]](/images/egov.png)
